31. System Security: Securing Networks Lesson Conclusion
ND545 C02 L02 A26 Lesson Conclusion V3
System Security: Securing Networks Lesson Conclusion Text
You made it! I told you this was a big lesson!
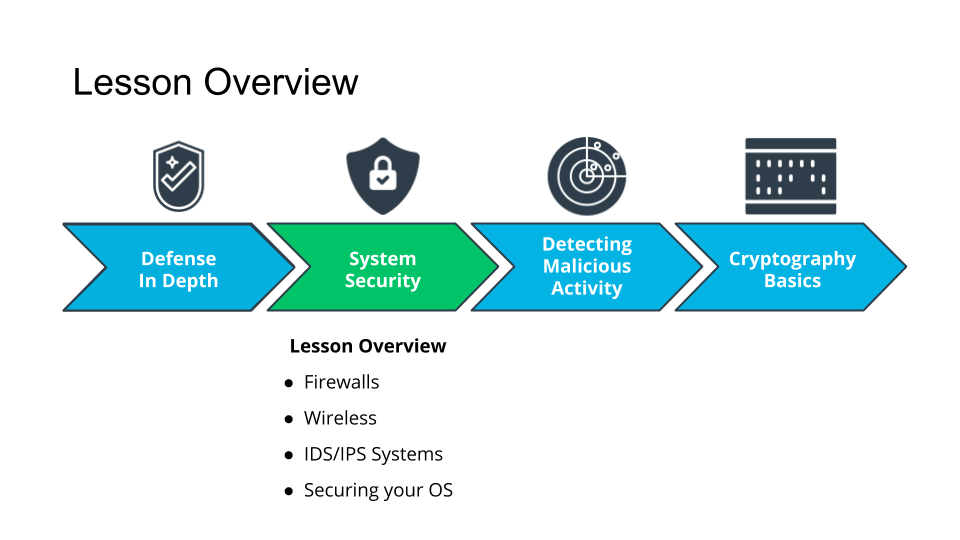
Recap
- We learned about firewalls and rules.
- We picked up best practices on wireless networks.
- We learned about IDS/IPS and signatures.
- Then we spent quite a bit of time with Windows and Linux.
You should feel proud of what you've accomplished so far. It was a lot to take in.
On to Lesson 3!
*As a side note, this course is a foundational course that is meant to help build the knowledge to become job-ready, but you will likely need additional training and/or coursework in order to obtain a job in this field. These foundations will set you up for success going forward and are vital to your success in this field. *
Lesson Overview
System Security: Securing Networks Lesson Conclusion Heading
Glossary and Resources
Here are all the terms we covered in this lesson:
| KeyTerm | Definition |
|---|---|
| 777 Permissions | Is a level of Linux permissions that means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone. |
| Authentication | the process or action of verifying the identity of a user or process |
| Automation | is the application of technology in the form of applications or processes to perform tasks, generally repetitive or time consuming, with minimal human input. |
| Blocklist | In computing, a denylist, or blocklist is a basic access control mechanism that allows through all elements except those explicitly mentioned. Those items on the list are denied access. |
| Daemons | is a computer program that runs as a background process, rather than being under the direct control of an interactive user. |
| Firewall | is a network device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic. |
| Firmware | is a software program or set of instructions programmed on a hardware device |
| Intrusion Detection System | is a device or application that monitors traffic for malicious activity or policy violations. |
| Next Gen Firewall | is a network security device that provides capabilities beyond a traditional, stateful firewall. While a traditional firewall typically provides stateful inspection of incoming and outgoing network traffic, a next-generation firewall includes additional features like application awareness and control, integrated intrusion prevention, and cloud-delivered threat intelligence |
| Repository | is a central location in which data is stored and managed. |
| SCCM | System Center Configuration Manager is a systems management software product developed by Microsoft for managing large groups of computers running Windows. |
| WSUS | Windows Server Update Services is a computer program and network service developed by Microsoft Corporation that enables administrators to manage the distribution of updates and hotfixes released for Microsoft products to computers in a corporate environment. |
| Yum | Yellowdog Updater, Modified is a free and open-source command-line package-management utility for Linux. It allows for automatic updates and package and dependency management. |